| Fachbereiche | |
|---|---|
| Buchreihen (97) |
1382
|
| Nachhaltigkeit |
3
|
| Gesundheitswesen |
1
|
| Geisteswissenschaften |
2377
|
| Naturwissenschaften |
5408
|
| Mathematik | 228 |
| Informatik | 320 |
| Physik | 980 |
| Chemie | 1364 |
| Geowissenschaften | 131 |
| Humanmedizin | 243 |
| Zahn-, Mund- und Kieferheilkunde | 10 |
| Veterinärmedizin | 108 |
| Pharmazie | 147 |
| Biologie | 835 |
| Biochemie, Molekularbiologie, Gentechnologie | 121 |
| Biophysik | 25 |
| Ernährungs- und Haushaltswissenschaften | 45 |
| Land- und Agrarwissenschaften | 1005 |
| Forstwissenschaften | 201 |
| Gartenbauwissenschaft | 20 |
| Umweltforschung, Ökologie und Landespflege | 148 |
| Ingenieurwissenschaften |
1798
|
| Allgemein |
98
|
|
Leitlinien Unfallchirurgie
5. Auflage bestellen |
|
Erweiterte Suche
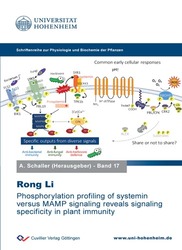
Phosphorylation profiling of systemin versus MAMP signaling reveals signaling specificity in plant immunity (Band 17)
Rong Li (Autor)Andreas Schaller (Herausgeber)
Vorschau
Leseprobe, PDF (2,2 MB)
Inhaltsverzeichnis, PDF (1,6 MB)
Plasma membrane-localized pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) detect both microbe-associated molecular patterns (MAMPs) such as flg22 and chitin, and host-derived signals like systemin. While early signaling events (phosphorylation, ROS burst, MAPK activation) are largely similar, they lead to different biological outcomes:
• MAMPs activate innate immunity,
• Systemin induces wound and herbivore defense responses.
To investigate how specificity arises, phospho-proteomics was applied in tomato cells (wild type vs. systemin receptor-deficient). In total, 4701 phospho-sites on 2119 proteins were identified. Using imputation and clustering, seven temporal phosphorylation patterns were observed:
• Systemin uniquely caused dephosphorylation at 1–15 min,
• flg22 triggered an early rapid phosphorylation response,
• Chitin mainly induced late phosphorylation events.
Specificity was illustrated by three protein groups:
1. RLCK/PBL kinases → different family members respond in an elicitor-specific way.
2. S-type anion channel SLAC1 → carries a single regulatory site, differentially phosphorylated depending on the elicitor.
3. Phosphatase PLL1a → has multiple elicitor-specific phospho-sites (flg22: Ser50–59, chitin: Ser86–89, systemin: Ser163–181).
Network analysis suggested that PLL1a regulates RBOHs, which was functionally validated using phospho-mimic/dead PLL1 mutants in Nicotiana.
| ISBN-13 (Printausgabe) | 9783689523114 |
| ISBN-13 (E-Book) | 9783689523121 |
| Buchendformat | A5 |
| Sprache | Englisch |
| Seitenanzahl | 144 |
| Umschlagkaschierung | glänzend |
| Auflage | 1. |
| Buchreihe | Schriftenreihe zur Physiologie und Biochemie der Pflanzen |
| Band | 17 |
| Erscheinungsort | Göttingen |
| Erscheinungsdatum | 06.08.2025 |
| Allgemeine Einordnung | Dissertation |
| Fachbereiche |
Biochemie, Molekularbiologie, Gentechnologie
Pflanzenproduktion |
| Schlagwörter | Biologie, Botanik, Biochemie, Pflanzenphysiologie, Tomate, Solanum lycopersicum, Peptidhormone, Peptidsignale, Systemin, flg22, Chitin, Phytocytokine, Mikroben-assoziiertes Molekulare Muster (MAMP), Immunantwort, Wundreaktion, Herbivore Insekten, Abwehr, CRISPR/Cas9, Phosphoproteomik, H+-ATPase, Protonenpumpe ähliche ulfopeptide, post-translationelle Modifizierung, Tyrosylprotein sulfotransferase, Transkriptionsfaktoren, Anthocyane, CLEL Peptide, Phytochrom, Phytochrome-interacting factor (PIF) constitutive photomorphogenesis (COP), Skotomorphogenese, Etioloement, Biology, Botany, Biochemistry, Plant Physiology, tomato, Solanum lycopersicum, peptide hormone, signaling peptide, systemin, flg22, chitin, phytocytokine, microbe-associated molecular pattern (MAMP), pattern-triggered immunity (PTI), wound response, insect herbivores, plant defense, CRISPR/Cas9, phospho proteomics, H+-ATPase, proton pump |